Irradiance
Irradiance is the power of electromagnetic radiation per unit area (radiative flux) incident on a surface. Radiant emittance or radiant exitance is the power per unit area radiated by a surface. The SI units for all of these quantities are watts per square meter (W/m2), while the cgs units are ergs per square centimeter per second (erg·cm−2·s−1, often used in astronomy). These quantities are sometimes called intensity, but this usage leads to confusion with radiant intensity, which has different units.
All of these quantities characterize the total amount of radiation present, at all frequencies. It is also common to consider each frequency in the spectrum separately. When this is done for radiation incident on a surface, it is called spectral irradiance, and has SI units W/m3, or commonly W·m−2·nm−1.
If a point source radiates light uniformly in all directions through a non-absorptive medium, then the irradiance decreases in proportion to the square of the distance from the object.
Contents |
Technical details
The irradiance of a monochromatic light wave in matter is given in terms of its electric field by [1]
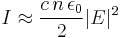 ,
,
where E is the complex amplitude of the wave's electric field, n is the refractive index of the medium, 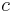 is the speed of light in vacuum, and ϵ0 is the vacuum permittivity. (This formula assumes that the magnetic susceptibility is negligible, i.e.
is the speed of light in vacuum, and ϵ0 is the vacuum permittivity. (This formula assumes that the magnetic susceptibility is negligible, i.e. 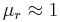 where
where 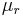 is the magnetic permeability of the light transmitting media. This assumption is typically valid in transparent media in the optical frequency range.)
is the magnetic permeability of the light transmitting media. This assumption is typically valid in transparent media in the optical frequency range.)
Irradiance is also the time average of the component of the Poynting vector perpendicular to the surface.
Solar energy
Irradiance due to solar radiation is also called insolation. The global irradiance on a horizontal surface on Earth consists of the direct irradiance Edir and diffuse irradiance Edif. On a tilted plane, there is another irradiance component: Eref, which is the component that is reflected from the ground. The average ground reflection is about 20% of the global irradiance. Hence, the irradiance Etilt on a tilted plane consists of three components: Etilt = Edir + Edif + Eref.[2]
The integral of solar irradiance over a time period is solar irradiation. Irradiation is measured in J/m2 and is represented by the symbol H.[2]
| Quantity | Symbol[nb 1] | SI unit | Symbol | Dimension | Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radiant energy | Qe[nb 2] | joule | J | M⋅L2⋅T−2 | energy | |||
| Radiant flux | Φe[nb 2] | watt | W | M⋅L2⋅T−3 | radiant energy per unit time, also called radiant power. | |||
| Spectral power | Φeλ[nb 2][nb 3] | watt per metre | W⋅m−1 | M⋅L⋅T−3 | radiant power per wavelength. | |||
| Radiant intensity | Ie | watt per steradian | W⋅sr−1 | M⋅L2⋅T−3 | power per unit solid angle. | |||
| Spectral intensity | Ieλ[nb 3] | watt per steradian per metre | W⋅sr−1⋅m−1 | M⋅L⋅T−3 | radiant intensity per wavelength. | |||
| Radiance | Le | watt per steradian per square metre | W⋅sr−1⋅m−2 | M⋅T−3 | power per unit solid angle per unit projected source area. confusingly called "intensity" in some other fields of study. |
|||
| Spectral radiance | Leλ[nb 3] or Leν[nb 4] |
watt per steradian per metre3 or watt per steradian per square |
W⋅sr−1⋅m−3 or W⋅sr−1⋅m−2⋅Hz−1 |
M⋅L−1⋅T−3 or M⋅T−2 |
commonly measured in W⋅sr−1⋅m−2⋅nm−1 with surface area and either wavelength or frequency. |
|||
| Irradiance | Ee[nb 2] | watt per square metre | W⋅m−2 | M⋅T−3 | power incident on a surface, also called radiant flux density. sometimes confusingly called "intensity" as well. |
|||
| Spectral irradiance | Eeλ[nb 3] or Eeν[nb 4] |
watt per metre3 or watt per square metre per hertz |
W⋅m−3 or W⋅m−2⋅Hz−1 |
M⋅L−1⋅T−3 or M⋅T−2 |
commonly measured in W⋅m−2⋅nm−1 or 10−22W⋅m−2⋅Hz−1, known as solar flux unit.[nb 5] |
|||
| Radiant exitance / Radiant emittance |
Me[nb 2] | watt per square metre | W⋅m−2 | M⋅T−3 | power emitted from a surface. | |||
| Spectral radiant exitance / Spectral radiant emittance |
Meλ[nb 3] or Meν[nb 4] |
watt per metre3 or watt per square |
W⋅m−3 or W⋅m−2⋅Hz−1 |
M⋅L−1⋅T−3 or M⋅T−2 |
power emitted from a surface per wavelength or frequency. |
|||
| Radiosity | Je or Jeλ[nb 3] | watt per square metre | W⋅m−2 | M⋅T−3 | emitted plus reflected power leaving a surface. | |||
| Radiant exposure | He | joule per square metre | J⋅m−2 | M⋅T−2 | ||||
| Radiant energy density | ωe | joule per metre3 | J⋅m−3 | M⋅L−1⋅T−2 | ||||
| See also: SI · Radiometry · Photometry | ||||||||
- ^ Standards organizations recommend that radiometric quantities should be denoted with a suffix "e" (for "energetic") to avoid confusion with photometric or photon quantities.
- ^ a b c d e Alternative symbols sometimes seen: W or E for radiant energy, P or F for radiant flux, I for irradiance, W for radiant emittance.
- ^ a b c d e f Spectral quantities given per unit wavelength are denoted with suffix "λ" (Greek) to indicate a spectral concentration. Spectral functions of wavelength are indicated by "(λ)" in parentheses instead, for example in spectral transmittance, reflectance and responsivity.
- ^ a b c Spectral quantities given per unit frequency are denoted with suffix "ν" (Greek)—not to be confused with the suffix "v" (for "visual") indicating a photometric quantity.
- ^ NOAA / Space Weather Prediction Center includes a definition of the solar flux unit (SFU).
See also
- Radiometry
- Spectral flux density
- Photometry (optics) Main Photometry/Radiometry article—explains technical terms
- Albedo
- Illuminance
- Fluence
- Insolation
- Light diffusion
- Solar azimuth angle
- Solar irradiation
- Solar constant
- Solar noon
- Stefan-Boltzmann law
References
- ^ Griffiths, David J. (1999). Introduction to electrodynamics (3. ed., reprint. with corr. ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ [u.a.]: Prentice-Hall. ISBN 0-13-805326-X. http://www.amazon.com/Introduction-Electrodynamics-3rd-David-Griffiths/dp/013805326X.
- ^ a b Quaschning, Volker (2003). "Technology fundamentals—The sun as an energy resource". Renewable Energy World 6 (5): 90–93. http://www.volker-quaschning.de/articles/fundamentals1/index_e.html.